802.11 Wireless Tools
aircrack-ng
aircrack-ng is an 802.11 WEP and WPA/WPA2-PSK key cracking program. It can recover the WEP key once enough encrypted packets have been captured with airodump-ng. This part of the aircrack-ng suite determines the WEP key using two fundamental methods. The first method is via the PTW approach (Pyshkin, Tews, Weinmann). The main advantage of the PTW approach is that very few data packets are required to crack the WEP key. The second method is the FMS/KoreK method. The FMS/KoreK method incorporates various statistical attacks to discover the WEP key and uses these in combination with brute forcing.
Additionally, the program offers a dictionary method for determining the WEP key. For cracking WPA/WPA2 pre-shared keys, a wordlist (file or stdin) or an airolib-ng has to be used.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 | |
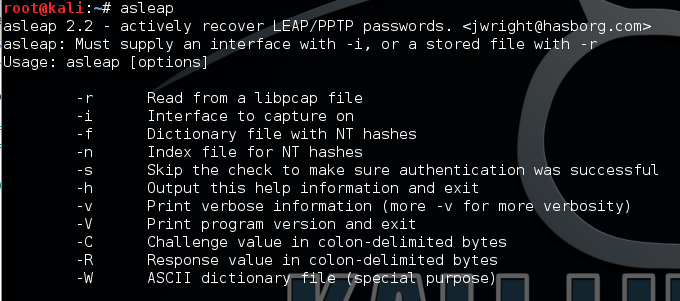
asleap
Actively recover LEAP/PPTP passwords
bully
Bully is a new implementation of the WPS brute force attack, written in C. It is conceptually identical to other programs, in that it exploits the (now well known) design flaw in the WPS specification. It has several advantages over the original reaver code. These include fewer dependencies, improved memory and cpu performance, correct handling of endianness, and a more robust set of options. It runs on Linux, and was specifically developed to run on embedded Linux systems (OpenWrt, etc) regardless of architecture.
Bully provides several improvements in the detection and handling of anomalous scenarios. It has been tested against access points from numerous vendors, and with differing configurations, with much success.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 | |
cowpatty
Implementation of an offline dictionary attack against WPA/WPA2 networks using PSK-based authentication (e.g. WPA-Personal). Many enterprise networks deploy PSK-based authentication mechanisms for WPA/WPA2 since it is much easier than establishing the necessary RADIUS, supplicant and certificate authority architecture needed for WPA-Enterprise authentication. Cowpatty can implement an accelerated attack if a precomputed PMK file is available for the SSID that is being assessed.
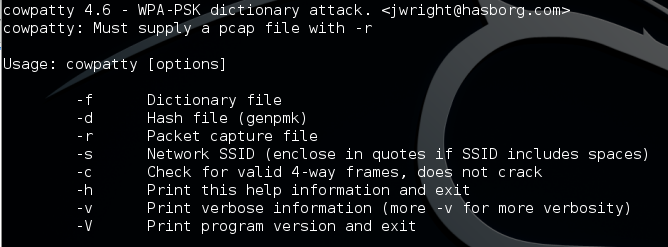
eapmd5pass
EAP-MD5 is a legacy authentication mechanism that does not provide sufficient protection for user authentication credentials. Users who authenticate using EAP-MD5 subject themselves to an offline dictionary attack vulnerability. This tool reads from a live network interface in monitor-mode, or from a stored libpcap capture file, and extracts the portions of the EAP-MD5 authentication exchange. Once the challenge and response portions have been collected from this exchange, eapmd5pass will mount an offline dictionary attack against the user’s password.
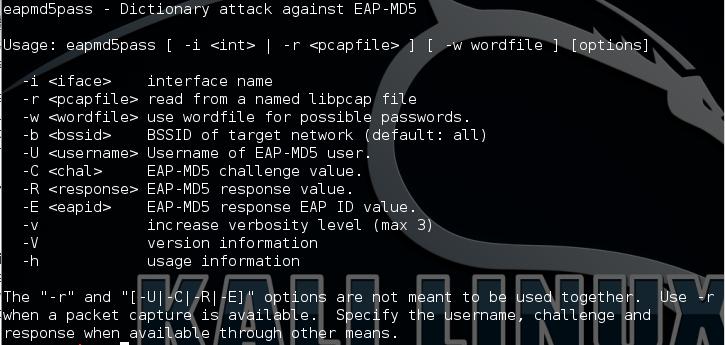
fern-wifi-cracker
Fern Wifi Cracker is a Wireless security auditing and attack software program written using the Python Programming Language and the Python Qt GUI library, the program is able to crack and recover WEP/WPA/WPS keys and also run other network based attacks on wireless or ethernet based networks.
Fern Wifi Cracker currently supports the following features:
WEP Cracking with Fragmentation,Chop-Chop, Caffe-Latte, Hirte, ARP Request Replay or WPS attack
WPA/WPA2 Cracking with Dictionary or WPS based attacks
Automatic saving of key in database on successful crack
Automatic Access Point Attack System
Session Hijacking (Passive and Ethernet Modes)
Access Point MAC Address Geo Location Tracking
Internal MITM Engine
Bruteforce Attacks (HTTP,HTTPS,TELNET,FTP)
Update Support
genkeys
Generates lookup file for asleap
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | |
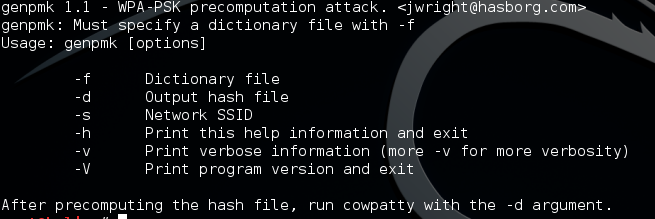
genpmk
WPA-PSK precomputation attack
giskismet
GISKismet is a wireless recon visualization tool to represent data gathered using Kismet in a flexible manner. GISKismet stores the information in a database so that the user can generate graphs using SQL. GISKismet currently uses SQLite for the database and GoogleEarth / KML files for graphing.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 | |
kismet
Kismet is an 802.11 layer2 wireless network detector, sniffer, and intrusion detection system. Kismet will work with any wireless card which supports raw monitoring (rfmon) mode, and (with appropriate hardware) can sniff 802.11b, 802.11a, 802.11g, and 802.11n traffic. Kismet also supports plugins which allow sniffing other media such as DECT.
Kismet identifies networks by passively collecting packets and detecting standard named networks, detecting (and given time, decloaking) hidden networks, and infering the presence of nonbeaconing networks via data traffic.
Kismet supports logging to the wtapfile packet format (readable by tcpdump and ethereal) and saves detected network information as plaintext, CSV, and XML. kismet is capable of using any GPS supported by gpsd and logs and plots network data.
mdk3
MDK is a proof-of-concept tool to exploit common IEEE 802.11 protocol weaknesses.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 | |
wifiarp
Wifi injection ARP answering tool based on Wifitap
wifidns
Wifi injection DNS answering tool based on Wifitap
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | |
wifi-honey
This script creates five monitor mode interfaces, four are used as APs and the fifth is used for airodump-ng. To make things easier, rather than having five windows all this is done in a screen session which allows you to switch between screens to see what is going on. All sessions are labelled so you know which is which.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | |
wifiping
Wifi injection based answering tool based on Wifitap
wifitap
Wifitap is a proof of concept for communication over WiFi networks using traffic injection.
Wifitap allows any application do send and receive IP packets using 802.11 traffic capture and injection over a WiFi network simply configuring wj0, which means :
setting an IP address consistent with target network address range
routing desired traffic through it
In particular, it’s a cheap method for arbitrary packets injection in 802.11 frames without specific library.
In addition, it will allow one to get rid of any limitation set at access point level, such as bypassing inter-client communications prevention systems (e.g. Cisco PSPF) or reaching multiple SSID handled by the same access point.
wifite
An automated wireless attack tool. To attack multiple WEP, WPA, and WPS encrypted networks in a row. This tool is customizable to be automated with only a few arguments. Wifite aims to be the “set it and forget it” wireless auditing tool.
Features
sorts targets by signal strength (in dB); cracks closest access points first
automatically de-authenticates clients of hidden networks to reveal SSIDs
numerous filters to specify exactly what to attack (wep/wpa/both, above certain signal strengths, channels, etc)
customizable settings (timeouts, packets/sec, etc)
“anonymous” feature; changes MAC to a random address before attacking, then changes back when attacks are complete
all captured WPA handshakes are backed up to wifite.py’s current directory
smart WPA de-authentication; cycles between all clients and broadcast deauths
stop any attack with Ctrl+C, with options to continue, move onto next target, skip to cracking, or exit
displays session summary at exit; shows any cracked keys
all passwords saved to cracked.txt
built-in updater: ./wifite.py -upgrade
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 | |
Bluetooth Tools
bluelog
Bluelog is a simple Bluetooth scanner that is designed to essentially do just one thing, log all the discoverable devices in the area. It is intended to be used as a site survey tool, identifying the number of possible Bluetooth targets there are in the surrounding environment.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 | |
bluemaho
BlueMaho is GUI-shell (interface) for suite of tools for testing security of bluetooth devices. It is freeware, opensource, written on python, uses wxPyhon. It can be used for testing BT-devices for known vulnerabilities and major thing to do – testing to find unknown vulns. Also it can form nice statistics.
Features:
scan for devices, show advanced info, SDP records, vendor etc
track devices – show where and how much times device was seen, its name changes
loop scan – it can scan all time, showing you online devices
alerts with sound if new device found
on_new_device – you can specify what command should it run when it founds new device
it can use separate dongles – one for scaning (loop scan) and one for running tools or exploits
send files
change name, class, mode, BD_ADDR of local HCI devices
save results in database
form nice statistics (uniq devices by day/hour, vendors, services etc)
test remote device for known vulnerabilities (see exploits for more details)
test remote device for unknown vulnerabilities (see tools for more details)
themes! you can customize it
blueranger
BlueRanger is a simple Bash script which uses Link Quality to locate Bluetooth device radios. It sends l2cap (Bluetooth) pings to create a connection between Bluetooth interfaces, since most devices allow pings without any authentication or authorization. The higher the link quality, the closer the device (in theory).
Use a Bluetooth Class 1 adapter for long range location detection. Switch to a Class 3 adapter for more precise short range locating. The recision and accuracy depend on the build quality of the Bluetooth adapter, interference, and response from the remote device. Fluctuations may occur even when neither device is in motion.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | |
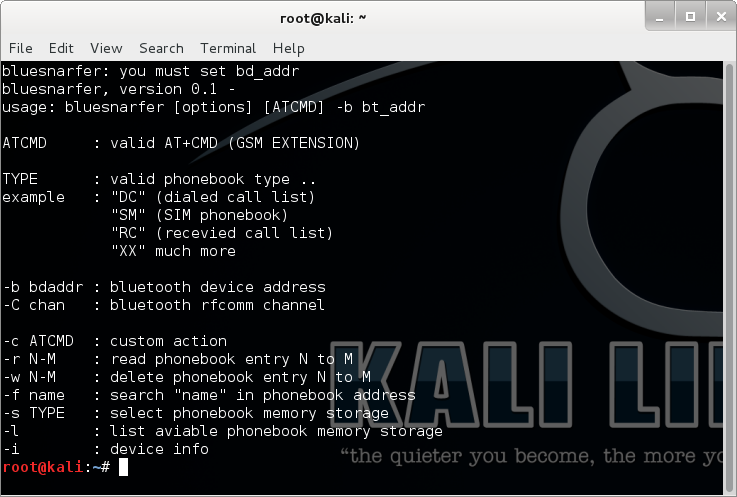
bluesnarfer
A Bluetooth bluesnarfing Utility.
btscanner
btscanner is a tool designed specifically to extract as much information as possible from a Bluetooth device without the requirement to pair. A detailed information screen extracts HCI and SDP information, and maintains an open connection to monitor the RSSI and link quality. btscanner is based on the BlueZ Bluetooth stack, which is included with recent Linux kernels, and the BlueZ toolset. btscanner also contains a complete listing of the IEEE OUI numbers and class lookup tables. Using the information gathered from these sources it is possible to make educated guesses as to the host device type.
1 2 3 4 5 | |
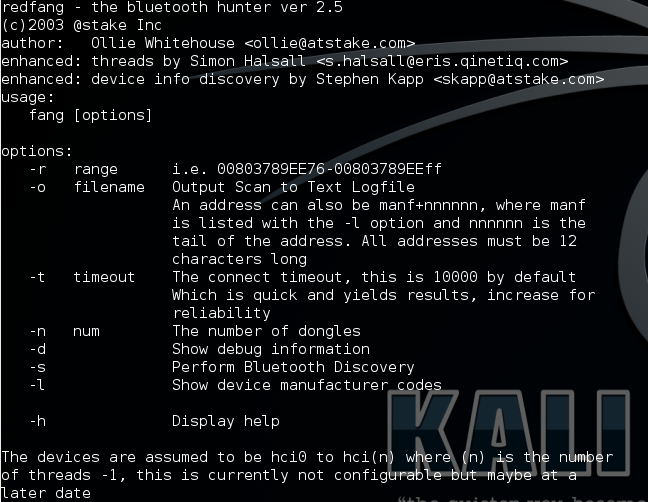
redfang
RedFang is a small proof-of-concept application to find non discoverable Bluetooth devices. This is done by brute forcing the last six (6) bytes of the Bluetooth address of the device and doing a read_remote_name().
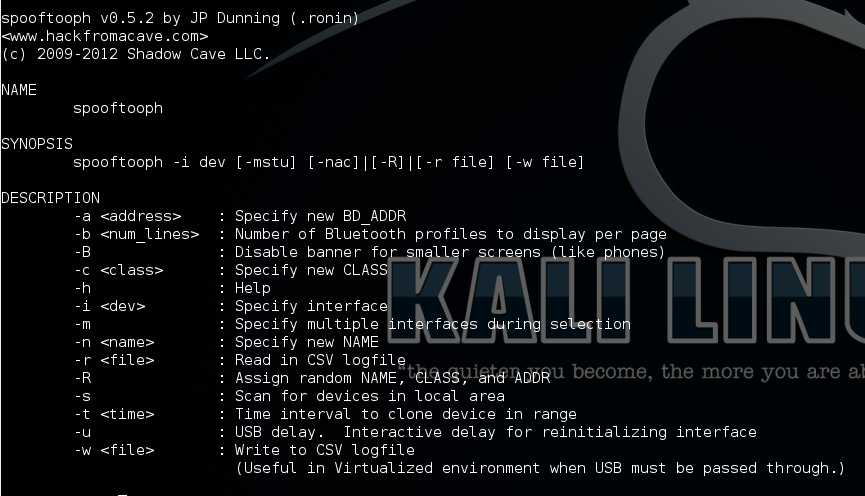
spooftooph
Spooftooph is designed to automate spoofing or cloning Bluetooth device information. Make a Bluetooth device hide in plain site.
Features:
Clone and log Bluetooth device information
Generate a random new Bluetooth profile
Change Bluetooth profile every X seconds
Specify device information for Bluetooth interface
Select device to clone from scan log
Other Wireless Tools
zbassocflood
Transmit a flood of associate requests to a target network.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | |
zbdsniff
Decode plaintext key ZigBee delivery from a capture file. Will process libpcap or Daintree SNA capture files.
1 2 3 4 | |
zbdump
A tcpdump-like tool for ZigBee/IEEE 802.15.4 networks
1 2 3 4 5 | |
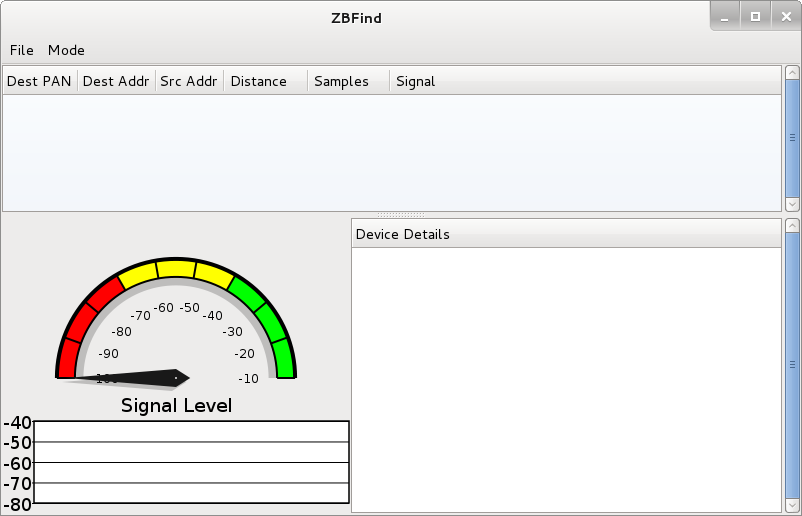
zbfind
zbfind provides a GTK-based GUI to the user which displays the results of a zbstumbler-like functionality. zbfind sends beacon requests as it cycles through channels and listens for a response, adding the response to a table as well as displaying signal strength on a gauge widget.
zbgoodfind
Search a binary file to identify the encryption key for a given SNA or libpcap IEEE 802.15.4 encrypted packet
1 2 3 4 5 6 | |
zbreplay
Replay ZigBee/802.15.4 network traffic from libpcap or Daintree files
1 2 3 4 5 | |
zbstumbler
Transmit beacon request frames to the broadcast address while channel hopping to identify ZC/ZR devices.
1 2 3 4 5 | |
RFID / NFC Tools
NFC Tools
mfcuk
Toolkit containing samples and various tools based on and around libnfc and crapto1, with emphasis on Mifare Classic NXP/Philips RFID cards. Special emphasis of the toolkit is on the following:
mifare classic weakness demonstration/exploitation
demonstrate use of libnfc (and ACR122 readers)
demonstrate use of Crapto1 implementation to confirm internal workings and to verify theoretical/practical weaknesses/attacks
mfoc
MFOC is an open source implementation of “offline nested” attack by Nethemba. This program allow to recover authentication keys from MIFARE Classic card. Please note MFOC is able to recover keys from target only if it have a known key: default one (hardcoded in MFOC) or custom one (user provided using command line).
mfterm
A terminal interface for working with Mifare tags.
The program is used as an interactive shell to read and write Mifare tags using libnfc and a libnfc compatible reader or to simply manipulate Mifare data dumps from files.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | |
mifare-classic-format
1 2 3 4 5 6 | |
nfc-list
nfc-list is a utility for listing any available tags like ISO14443-A, FeliCa, Jewel or ISO14443-B (according to the device capabilities). It may detect several tags at once thanks to a mechanism called anti-collision but all types of tags don’t support anti-collision and there is some physical limitation of the number of tags the reader can discover.
This tool displays all available information at selection time.
1 2 3 | |
nfc-mfclassic
nfc-mfclassic is a MIFARE Classic tool that allow to read or write DUMP file using MIFARE keys provided in KEYS file.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | |
RFIDiot ACG
RFIDiot FROSCH
RFIDiot PCSC
A collection of tools and libraries for exploring RFID technology, written in Python.
ChAP.py
Script that tries to select the EMV Payment Systems Directory on all inserted cards.
bruteforce.py
Try random numbers to login to sector 0
cardselect.py
Select card and display ID
copytag.py
Read all sectors from a standard tag and write them back to a blank
demotag.py
Test IAIK TUG DemoTag
eeprom.py
Display reader’s eeprom settings
fdxbnum.py
Generate / decode FDX-B EM4x05 compliant IDs
formatmifare1kvalue.py
Format value blocks on a mifare standard tag
froschtest.py
Test frosch HTRM112 reader
hidprox.py
Show HID Prox card type and site/id code
hitag2brute.py
Brute Force hitag2 password
hitag2reset.py
Reset hitag2 password
isotype.py
Determine ISO tag type
jcopmifare.py
Test program for mifare emulation on JCOP
jcopsetatrhist.py
Set ATR History bytes on JCOP cards
jcoptool.py
JCOP card toolkit
lfxtype.py
Select card and display tag type
loginall.py
Attempt to login to each sector with transport keys
mifarekeys.py
Calculate 3DES key for Mifare access on JCOP cards
mrpkey.py
Calculate 3DES key for Machine Readable Passport
multiselect.py
Continuously select card and display ID
nfcid.py
Python code for Identifying NFC cards
pn532emulate.py
Switch NXP PN532 reader chip into TAG emulation mode
pn532mitm.py
NXP PN532 Man-In-The_Middle – log conversations between TAG and external reader
q5reset.py
Reset q5 tag
readlfx.py
Read all sectors from a LFX reader
readmifare1k.py
Read all sectors from a mifare standard tag
readmifaresimple.py
Read all sectors from a mifare tag
readmifareultra.py
Read all sectors from a Ultralight tag
readtag.py
Read all sectors from a standard tag
rfidiot-cli.py
CLI for rfidiot
send_apdu.py
Python code for Sending raw APDU commands
sod.py
Try to find X509 data in EF.SOD
transit.py
Generate / decode FDI Matalec Transit 500 and Transit 999 UIDs
unique.py
Generate EM4x02 and/or UNIQUE compliant IDs
writelfx.py
Read and then write all sectors from a LFX reader
writemifare1k.py
Write all blocks on a mifare standard tag
Check http://rfidiot.org/ for more information and examples
Software Defined Radio
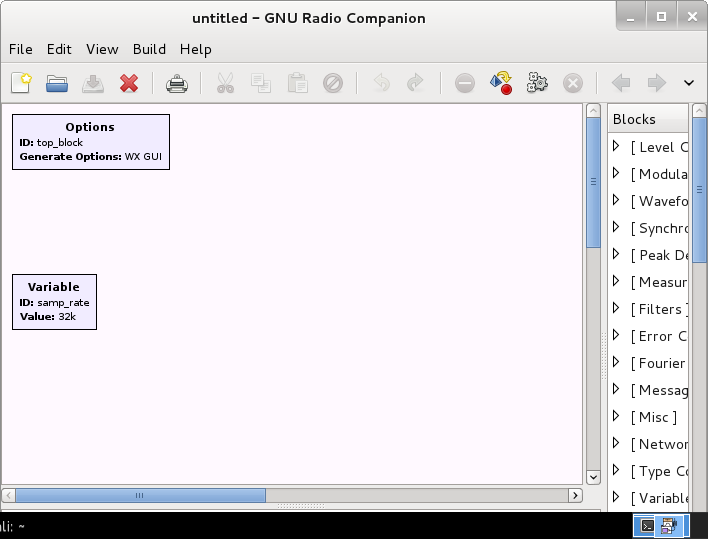
gnuradio-companion
A graphical tool for creating signal flow graphs and generating flow-graph source code.
gqrx
Gqrx is a software defined radio receiver powered by the GNU Radio SDR framework and the Qt graphical toolkit. Gqrx supports many of the SDR hardware available, including Funcube Dongles, rtl-sdr, HackRF and USRP devices.
Currently it works on Linux and Mac and supports the following devices:. Funcube Dongle Pro and Pro+ RTL2832U-based DVB-T dongles (rtlsdr via USB and TCP) OsmoSDR USRP HackRF Jawbreaker Nuand bladeRF any other device supported by the gr-osmosdr library
The latest stable version of Gqrx is 2.2, it is available for Linux, FreeBSD and Mac and it offers the following features:
Discover devices attached to the computer.
Process I/Q data from the supported devices.
Change frequency, gain and apply various corrections (frequency, I/Q balance).
AM, SSB, FM-N and FM-W (mono and stereo) demodulators.
Special FM mode for NOAA APT.
Variable band pass filter.
AGC, squelch and noise blankers.
FFT plot and waterfall.
Record and playback audio to / from WAV file.
Spectrum analyzer mode where all signal processing is disabled.
gr-scan
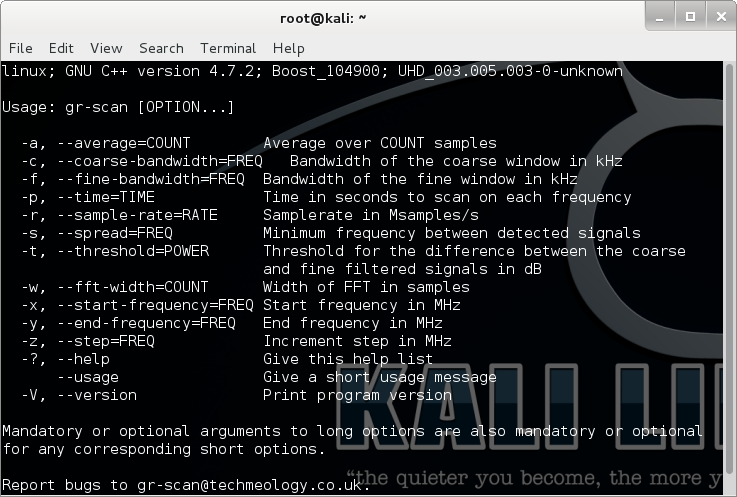
gr-scan is a program written in C++, and built upon GNU Radio, rtl-sdr, and the OsmoSDR Source Block. It is intended to scan a range of frequencies and print a list of discovered signals. It should work with any device that works with that block, including Realtek RTL2832U devices. This software was developed using a Compro U620F, which uses an E4000 tuner
modes_gui
Part of gr-air-modes
gr-air-modes implements a software-defined radio receiver for Mode S transponder signals, including ADS-B reports from equipped aircraft.
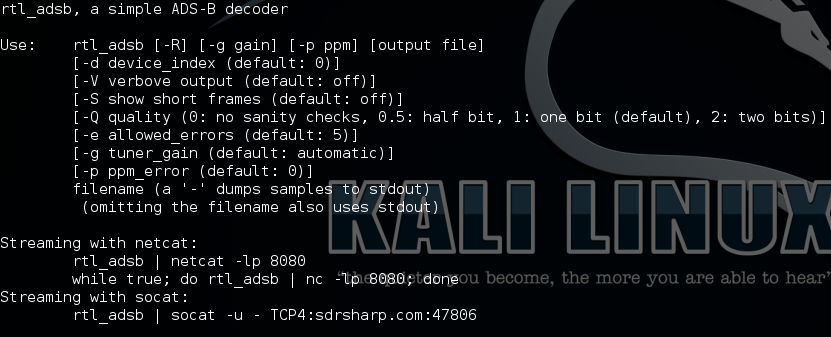
rtl_adsb
A simple ADS-B decoder
rtl_fm
A simple narrow band FM demodulator for RTL2832 based DVB-T receivers
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 | |
rtl_sdr
An I/Q recorder for RTL2832 based DVB-T receivers
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | |
rtlsdr-scanner
A cross platform Python frequency scanning GUI for USB TV dongles, using the OsmoSDR rtl-sdr library. In other words a cheap, simple Spectrum Analyser. The scanner attempts to overcome the tuner’s frequency response by averaging scans from both the positive and negative frequency offets of the baseband data.
rtl_tcp
An I/Q spectrum server for RTL2832 based DVB-T receivers
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | |
rtl_test
A benchmark tool for RTL2832 based DVB-T receivers
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | |
Noise proves nothing. Often a hen who has merely laid an egg cackles as if she laid an asteroid.
— Mark Twain